Hydrogen Fuels UK: Government Policy, Standards, and Support for Hydrogen Mobility
The UK government views hydrogen fuels as a key part of its plan to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, especially in transport. Through various policies, rules, and funding programs, the government is promoting the development of a low-carbon hydrogen economy that supports clean mobility and sustainable transport solutions.
Strategic Policy Frameworks Supporting Hydrogen Mobility
UK Hydrogen Strategy (2021, updated ongoing)
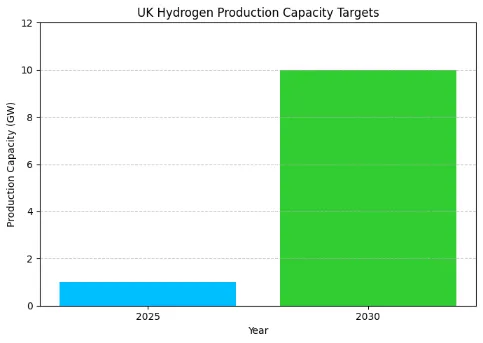
This major policy highlights the government’s goal to increase low-carbon hydrogen production to 10GW by 2030, with a target of 1GW by 2025. The strategy points out hydrogen’s importance in areas like transport, industry, and power. It details step-by-step plans for production, infrastructure, and uses, such as buses, trains, and heavy goods vehicles.
Energy White Paper & CCUS Integration
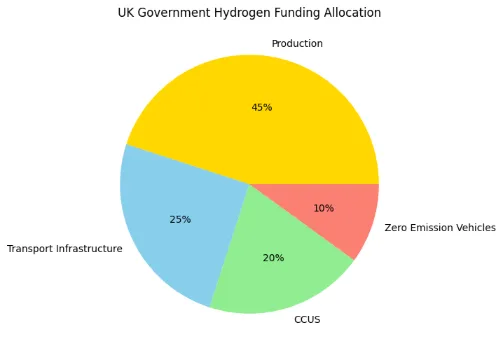
The UK’s Energy White Paper dedicates £1 billion to support carbon capture, usage, and storage (CCUS) technologies, essential for producing ‘blue’ hydrogen with low emissions. The government is focusing on industrial clusters, especially those near coastlines, for early CCUS efforts, combining hydrogen production with carbon storage to reduce emissions in transport and industry.
Hydrogen Business Models and Funding
The government has set up contract-for-difference style business models to encourage private investment in hydrogen production and infrastructure. The Low Carbon Hydrogen Agreements (LCHA) and the Net Zero Hydrogen Fund (NZHF) offer financial help to expand electrolytic hydrogen projects and refuelling infrastructure.
Sector-Specific Support
The Zero Emission Bus Regional Areas (ZEBRA) scheme is providing over £120 million to roll out up to 4,000 zero-emission buses, including hydrogen fuel cell buses, along with the necessary infrastructure. Similar targeted funding is available for hydrogen in rail, maritime, and heavy goods vehicles to speed up adoption.
Development of Standards and Regulatory Frameworks
Low Carbon Hydrogen Standard
The UK is working on standards to define ‘low carbon hydrogen’, ensuring that hydrogen fuels meet strict emissions criteria. This standard affects funding eligibility and boosts market confidence in hydrogen’s environmental advantages.
Safety and Operational Guidelines
Regulatory bodies are partnering with industry to set safety rules for hydrogen production, storage, transport, and refuelling. This includes tackling issues in maritime hydrogen vessel certification and on-road vehicle regulations.
Strategic Planning and Market Design
The government’s ongoing consultations and policy updates focus on mixing hydrogen into existing gas networks, planning hydrogen transport corridors, and creating business models for storage and distribution infrastructure. This ensures a connected and scalable hydrogen mobility system.
Government and Industry Collaboration
The UK government collaborates closely with industry groups, research organizations, and local authorities to test hydrogen mobility projects, develop infrastructure, and create demand. Initiatives like the Hydrogen Energy Association’s action plan aim to organize efforts across transport, industry, and power sectors to grow hydrogen use effectively.
Regional hydrogen clusters are being formed to create concentrated hubs for demand and supply. These clusters support buses, commercial fleets, rail, and other transport types, promoting local economic growth and innovation.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Emissions Reduction
Hydrogen fuels help reduce transport emissions, improve air quality, and boost energy security by diversifying fuel sources.
Cost Savings
The government estimates that hydrogen-enabled transport and industry could save between £13 billion and £24 billion by 2050 through flexible, low-carbon energy solutions.
Job Creation
The hydrogen sector presents a major economic opportunity, with investments likely to create thousands of skilled jobs in production, infrastructure, and vehicle manufacturing.
Energy Security
By developing domestic hydrogen production, the UK reduces its reliance on imported fossil fuels and strengthens its energy independence.
For more information on UK hydrogen initiatives, see the official government announcement and learn about hydrogen technology from the Institution of Gas Engineers and Managers.
Conclusion
The UK government’s policy framework, funding programs, and regulatory standards are creating a supportive setting for hydrogen fuels to grow in the transport sector. By combining hydrogen production with CCUS, establishing clear standards, and encouraging public-private partnerships, the UK is speeding up the shift to hydrogen-powered mobility, positioning itself as a global leader in clean transport innovation.
Hydrogen Energy Case Studies & Resources
Explore these real-world applications and strategic documents about hydrogen technology:
Hydrogen Refuelling Case Studies
Fuel Cell Systems showcases practical implementations of hydrogen refuelling solutions across various industries.
Source: Fuel Cell Systems UKTees Valley Hydrogen Transport Project
A case study on hydrogen-powered transport initiatives in the Tees Valley region of the UK.
Source: CenexHydrogen-Powered HGV Innovation
Case study about an innovative hydrogen-powered heavy goods vehicle developed in Glasgow.
Source: Glasgow City of Science & InnovationUK Hydrogen Strategy
The official UK government publication outlining the national strategy for hydrogen energy development.
Source: UK GovernmentNote: These links are external resources and will take you to third-party websites.